- Home
- New Patients
- Treatments
- All Treatments
- Physiotherapy Evaluation
- Vestibular rehabilitation
- Cervicocranial treatment
- LVLA – Low Velocity Low Amplitude
- HVLA – High Velocity Low Amplitude
- Modern Cupping Treatment
- Kinesio Taping
- Kinetic Flossing
- IASTM – Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Dry Needling
- Electro Dry Needling
- Manual Therapy
- Therapeutic Exercises
- Low Level Laser Treatment
- About Aleks
- Blog
- F&Q
- Contact
- Home
- New Patients
- Treatments
- All Treatments
- Physiotherapy Evaluation
- Vestibular rehabilitation
- Cervicocranial treatment
- LVLA – Low Velocity Low Amplitude
- HVLA – High Velocity Low Amplitude
- Modern Cupping Treatment
- Kinesio Taping
- Kinetic Flossing
- IASTM – Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Dry Needling
- Electro Dry Needling
- Manual Therapy
- Therapeutic Exercises
- Low Level Laser Treatment
- About Aleks
- Blog
- F&Q
- Contact
Physiotherapy Evaluation

A physiotherapy assessment, also known as a physical therapy evaluation, is a systematic and thorough evaluation performed by a physiotherapist to assess a patient’s physical health, functional abilities, and any musculoskeletal or neurological issues. The assessment provides essential information that helps the physiotherapist develop an appropriate treatment plan to address the patient’s specific needs. Here’s a breakdown of what’s involved in a physiotherapy assessment:
1. Patient History: The physiotherapist will begin by taking a detailed medical history, which includes information about the patient’s current symptoms, past medical conditions, surgeries, medications, and relevant family medical history. Understanding the patient’s medical background helps the physiotherapist to identify potential contributing factors to the current condition.
2. Subjective Assessment: This part involves the physiotherapist engaging in a conversation with the patient to gather subjective information about their current complaint. The patient will be asked about the location, duration, and intensity of pain or discomfort, as well as any specific activities or movements that exacerbate or relieve the symptoms.
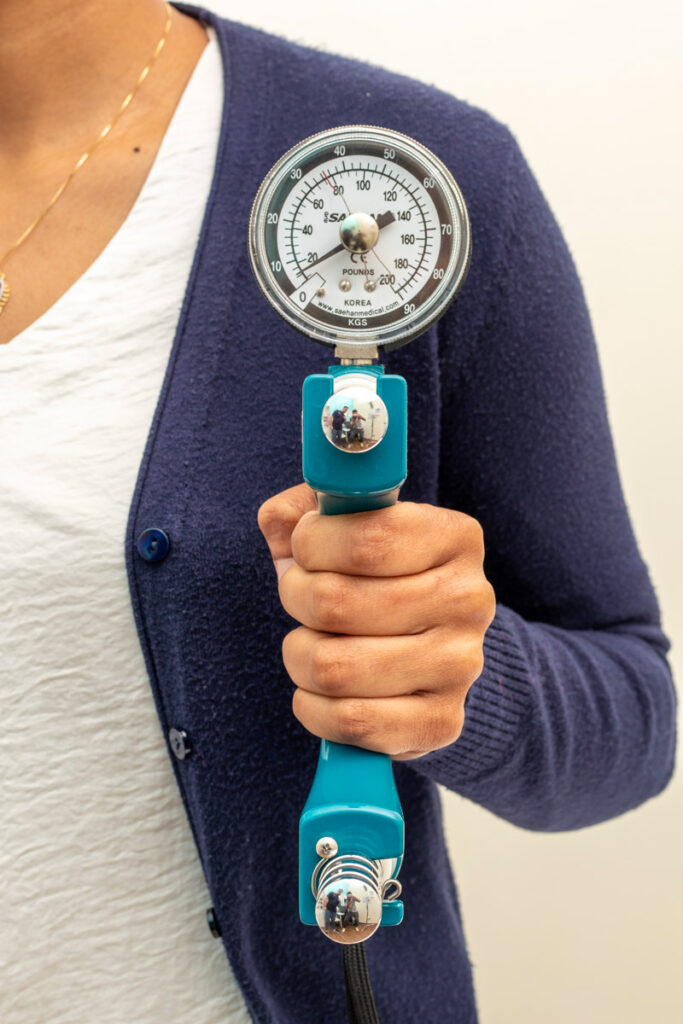
3. Objective Assessment: The objective assessment is a physical examination conducted by the physiotherapist to evaluate the patient’s physical function, strength, range of motion, and any physical limitations. This may include:
o Range of Motion (ROM) Measurement: The physiotherapist will assess the movement and flexibility of joints and muscles.
o Muscle Strength Testing: The strength of various muscle groups will be evaluated through specific movements or resistance exercises.
o Posture and Alignment Assessment: The physiotherapist will observe the patient’s posture and alignment while standing, sitting, or lying down.
o Balance and Coordination Evaluation: The patient’s balance and coordination abilities may be assessed through various tests and exercises.
o Neurological Assessment: If relevant, the physiotherapist may perform neurological tests to check for any nerve-related issues.
4. Special Tests: Depending on the patient’s condition, additional tests may be conducted to target specific problem areas, such as ligament stability tests or joint-specific assessments.
5. Functional Assessment: The physiotherapist will evaluate the patient’s ability to perform functional activities relevant to their daily life, work, or sports, based on their individual goals and needs.
6. Diagnosis: After analyzing the information gathered during the assessment, the physiotherapist will provide a diagnosis or a clinical impression of the patient’s condition.
7. Treatment Plan: Following the assessment, the physiotherapist will discuss the findings with the patient and develop a personalized treatment plan. The plan will include specific therapeutic interventions, exercises, manual therapy techniques, and education to address the patient’s unique needs and goals.
Throughout the assessment, the physiotherapist will communicate with the patient, explaining the process and findings, and may also answer any questions or concerns the patient may have. The goal is to create a collaborative approach to treatment and empower the patient to actively participate in their recovery.
Having a spine Problem? Try Our Therapy Today
“Empower your body’s journey to wellness. Book your physiotherapy session today and embrace a pain-free, active life.”
Spinal stenosis
Herniated disc
Disc Bulge